Works
Portfolio Single
Portfolio
Deploying a highly Scalable and Available three-Tier web application with AWS and Terraform
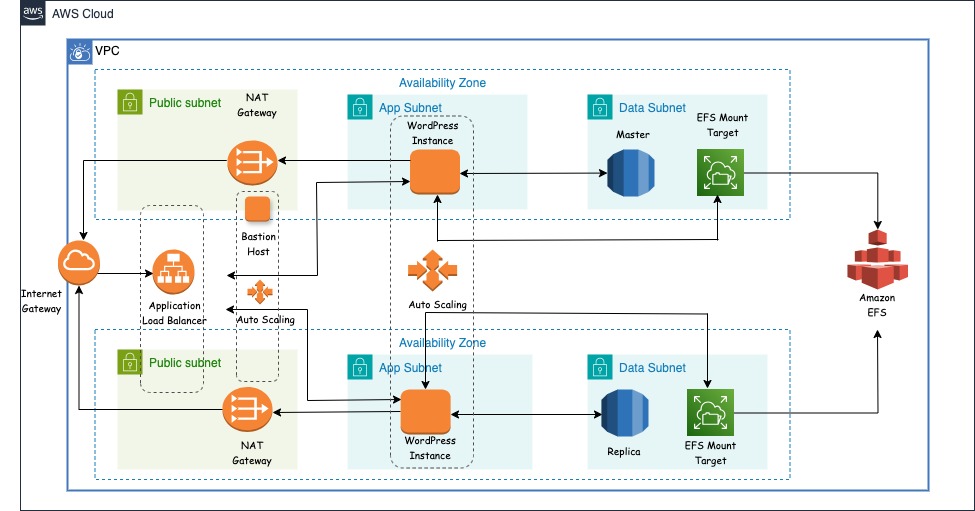
This project focuses on designing and deploying a highly scalable, highly available, and secure three-tier web application architecture on Amazon Web Services (AWS) using Terraform as the Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool.
The three-tier architecture—comprising presentation (web), application (logic), and data (database) layers—is a widely adopted model for building robust, modular, and scalable applications. Leveraging AWS cloud-native services and Terraform automation, this project showcases how to build and manage modern cloud infrastructure that is production-ready.
• Configured Amazon VPC for secure networking.
• Deployed a multi-tier web application using Amazon EC2 instances.
• Integrated Amazon RDS for a reliable database backend.
• Used Amazon EFS for scalable and shared file storage.
Here's a clear overview of the project designed to inspire and provide valuable insights!
Setting Up the Amazon VPC
• Designed a custom VPC with public and private subnets for optimal security.
• Configured routing tables, NAT gateways, and internet gateways to manage traffic flow.
• Implemented security groups to control access to resources.
Configuring Amazon EC2 for Compute Resources
• Launched EC2 instances in the private subnet to host the application.
• Configured auto-scaling groups to ensure the application could handle variable traffic loads.
• Used Application Load Balancer (ALB) to distribute traffic across instances for high availability.
Deploying Amazon RDS for Database Management
• Set up a managed relational database using Amazon RDS.
• Configured Multi-AZ deployment for automatic failover and data redundancy.
• Optimized performance with read replicas for handling read-heavy workloads.
Integrating Amazon EFS for Shared Storage
• Created an Amazon EFS file system for shared and scalable storage.
• Mounted EFS on EC2 instances to enable seamless file sharing across the application.
• Ensured high availability by deploying EFS across multiple Availability Zones.
AWS Services and Tools Used
• Amazon VPC: Provides secure networking for resources.
• Amazon EC2: Offers scalable compute capacity for hosting applications.
• Amazon RDS: Simplifies database management with high availability.
• Amazon EFS: Enables scalable and shared storage for the application.
• NAT Gateway: Provides secure internet access for instances residing in private subnets.
• Application Load Balancer: Distributes traffic efficiently for fault tolerance.
Best Practices for Building Highly Available Applications
• Design for Redundancy: Use Multi-AZ deployments and load balancers to avoid single points of failure.
• Automate Scaling: Leverage auto-scaling to handle variable traffic loads.
• Secure Resources: Implement security groups, IAM roles, and encryption for data protection.
• Monitor Continuously: Use tools like CloudWatch to track application health and performance.